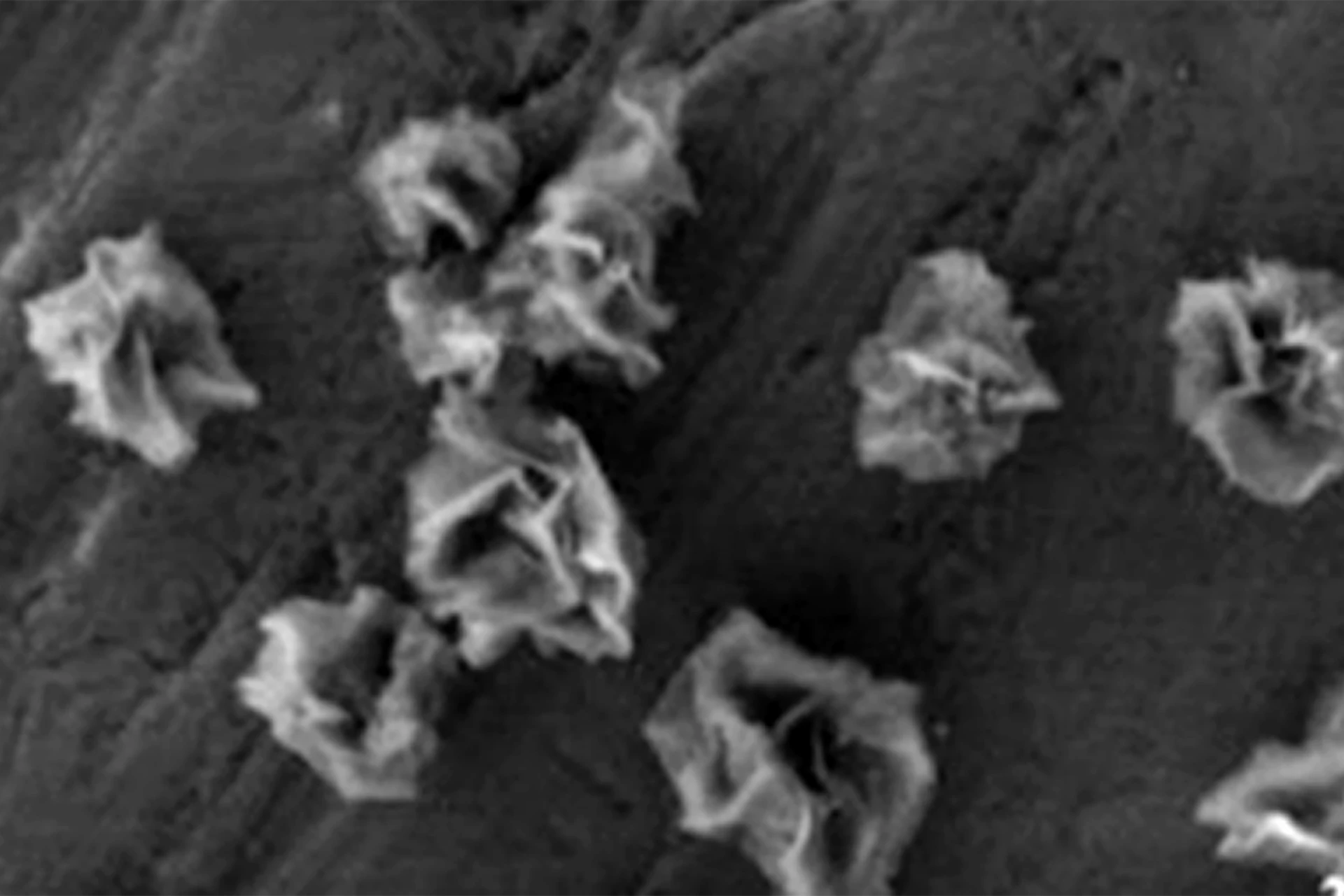
Scientists from the University of Texas University of A&M have developed special nanoparticles in the form of flowers – “nanocaves”. These structures help to protect and restore brain cells, reduce oxidative stress and improve the work of mitochondria.
In the studies, two types of “nannetons” from disulfide and dyslenide molybdenum (Mos₂ and Mose₂) were used. In experiments on cells, they quickly penetrated into neurons and astrocytes, stimulated cell growth (MOS₂ – up to 93% in neurons) and significantly reduced the level of harmful active forms of oxygen (mose₂ – up to 80%). These molecules damage cells in large quantities and cause inflammation.
Also, “nanocaves” almost completely prevented damage to mitochondria and activated the genes responsible for their restoration. In experiments on microscopic worms, C. Elegans Mose₂ increased life expectancy by a third, mos₂ – gave a lower but also positive effect.
So far, the work was mainly carried out in the laboratory and on model organisms, so the results are not guaranteed to be suitable for people. With very high doses of MOSE₂, a slight decrease in cell viability was observed, which indicates the need for accurate dosage selection.
News -in -law materials cannot be equated to the doctor’s prescription. Before making a decision, consult a specialist.