The National Guard is a structure that occupies a special place between the army and the police, raising questions about its purpose and functions. The expert of the heading about the military technologies of the Ferra.ru website Pavel Voronov told why the National Guard exists and what tasks it solves against the background of other law enforcement agencies.
The history of the National Guard began during the Great French Revolution, when there was a need to create an armed militia, capable of maintaining order in the conditions of instability. According to Voronov, this was an attempt to form a “folk” force that would unite citizens who share common values, language and culture. So the “bourgeois police” appeared, later renamed the National Guard. She obeyed the local authorities, and its participants often provided themselves with weapons and ammunition. Unlike the regular army, the National Guard was originally created to solve internal problems, such as the protection of order in crisis times, when the police or the army could not cope. In revolutionary France, the National Guard became the basis for the formation of a new army, and later turned into a reserve for protecting the country from external threats. After Napoleon’s defeats in 1812-1814, the National Guard actively replenished the army and participated in the defense of the territory.
Thus, earlier the National Guard performed tasks that went beyond the functions of the army and the police:
- Maintaining order in crises. When the police could not cope with the riots or revolutionary unrest, the National Guard provided stability using more serious weapons.
- Reserve for the army. In the conditions of war, when regular troops were busy at the front, the National Guard served as a reserve to protect the territory or replenish the army units.
- Counterweight to the authorities. In revolutionary periods, for example, in France, the National Guard was formed as an alternative to the royal army, obeying local or new authorities.
- Recruit training. The National Guard prepared recruits for the army, especially in the conditions of lack of professional soldiers.
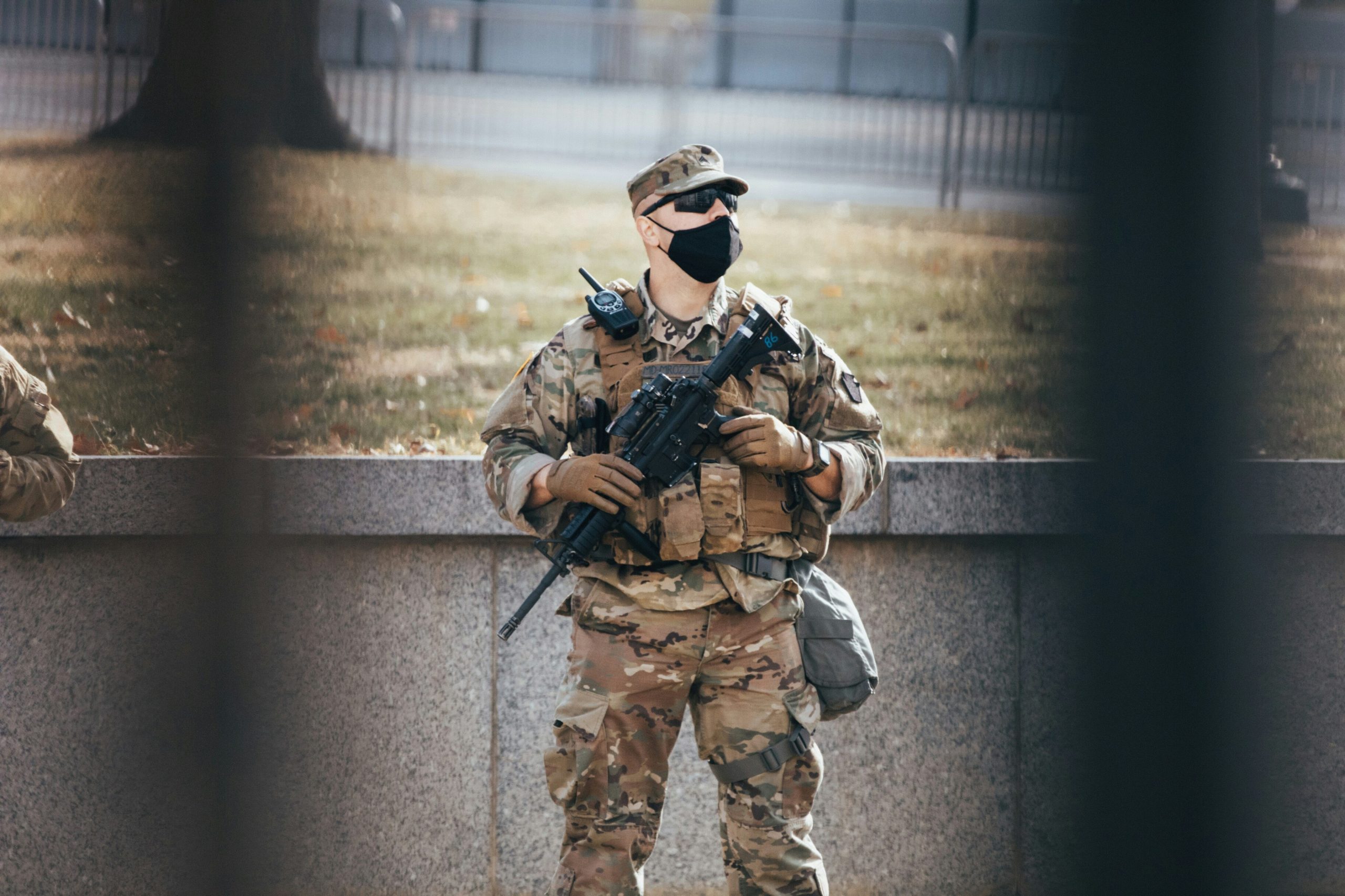
In the USA, the National Guard is one of the largest and most combat -ready in the world, numbering about 430 thousand people. It includes the army and the Air Force, and the plans for the creation of space forces. The National Guards are subordinate to both the state authorities and the federal government, which makes them a unique tool for solving both local and national problems. For example, on August 13, 2025, the US President introduced the National Guard to Washington to support the police, which caused disputes about the possible replacement of local law enforcement agencies.
The National Guard of the United States is equipped with volunteers who undergo military training on weekends or at short -term training camps. This allows citizens to maintain their status, but to be prepared for mobilization in case of emergency situations. Among the motives for the service are benefits, medical insurance and educational loans. The equipment of the National Guard is often inferior to the regular army: outdated models of tanks, armored vehicles and rifles are used, although aviation includes transport aircraft and helicopters for rescue operations.
The US National Guard is actively involved in military conflicts abroad, such as the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, where it provided up to 55% of personnel. Voronov emphasized that the National Guards are assuming the tasks of the second line: the protection of the rear, control of the territories and training of local forces.
In Russia, the National Guard, or the Russian Guard, has a different nature. It was created on the basis of the internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and performs functions similar to the gendarmerie. The Russian Guard is equipped with heavy equipment, including an armored personnel carrier and BMP, and is involved in the fight against terrorism and internal conflicts. Unlike the American model, it is equipped with recruits and contractors, and not volunteers, and acts as a full -fledged combat structure. In the modern world, the tasks of the National Guard were adapted to new challenges:
- The fight against internal threats. The National Guard, especially in Russia, is involved in counteracting terrorism and suppressing internal conflicts, where the police may not be equipped.
- Participation in rescue operations. In the United States, the National Guard actively helps with natural disasters, such as hurricanes or fires, complementing civil services.
- Support for the army in conflicts. The National Guard of the United States participates in foreign operations, performing the functions of protection, patrolling and preparing local forces, which reduces the load on the regular army.
- Flexibility in subordination. Dual subordination (local and federal authorities of the United States) allows the National Guard to quickly respond to regional and national threats.
- Reserve of personnel. The National Guard prepares reservists that can be mobilized to strengthen the army in the case of large conflicts.
Today, the National Guard remains an important part of the power structures, especially in countries with small armies. Its role in the USA and Russia is different: in America it is a reserve for military and rescue operations, in Russia – a full -fledged power structure with army tasks.